Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by the rapid proliferation of skin cells, leading to thick, red, scaly patches that can be painful and emotionally distressing. Traditional treatments often focus on managing symptoms rather than addressing the underlying causes of the disease, and they can come with significant side effects. However, the emerging field of regenerative medicine offers new hope through the use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which have shown promising results in recent studies.
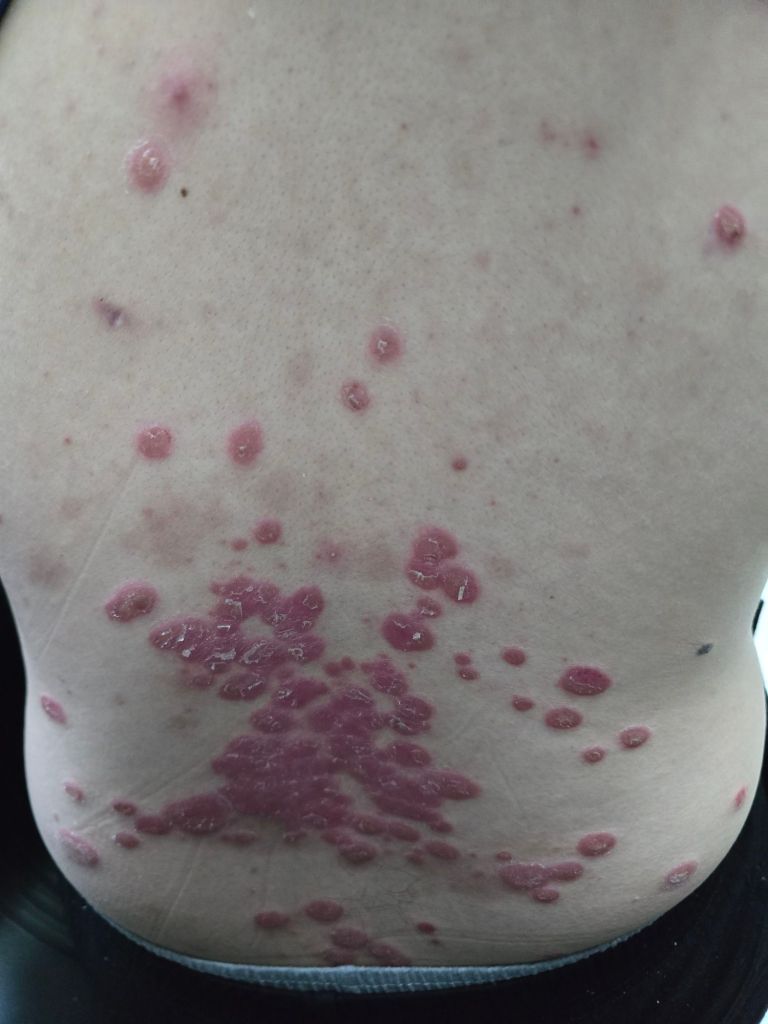
What Are Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)?
MSCs are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate into various cell types, including bone, cartilage, and fat cells. They are found in several tissues, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord tissue. One of the most intriguing properties of MSCs is their ability to modulate the immune system, making them particularly valuable in treating autoimmune diseases like psoriasis.
Overview of Key Studies
Two recent studies have highlighted the potential of MSCs, particularly umbilical mesenchymal stem cells (UMSCs), in treating psoriasis:
- “Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Psoriasis: Systematic Review”
This comprehensive review examines the potential of MSCs to treat psoriasis by modulating the immune system. The study discusses how MSCs can decrease inflammation and reduce the severity of psoriasis symptoms. Patients treated with MSCs have shown significant improvement in their skin conditions, with some experiencing long-term remission. The review also highlights the safety profile of MSC therapy, which is crucial for its application in chronic conditions like psoriasis【7†source】. - “Therapeutic Effects of UMSCs in Inflammatory Skin Diseases”
This study focuses specifically on UMSCs, exploring their effectiveness in treating psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. UMSCs are highlighted for their strong anti-inflammatory properties, which help alleviate the symptoms of psoriasis. The study found that UMSCs could significantly reduce the inflammatory response associated with psoriasis, leading to improved skin condition and patient quality of life. This research suggests that UMSCs could be a viable treatment option for patients who have not responded well to traditional therapies【7†source】.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which MSCs exert their therapeutic effects in psoriasis is multifaceted. MSCs are known to secrete various bioactive molecules, including anti-inflammatory cytokines, growth factors, and extracellular vesicles. These molecules work together to modulate the immune system, reduce inflammation, and promote tissue repair.
- Immunomodulation: MSCs can suppress the activity of pro-inflammatory T cells and promote the generation of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which help maintain immune tolerance. This is particularly important in psoriasis, where the immune system is dysregulated, leading to excessive skin cell proliferation.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: MSCs secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β, which help reduce the inflammatory response in psoriatic lesions. This reduction in inflammation can lead to a decrease in the severity of skin symptoms and a reduction in the overall disease burden.
- Tissue Regeneration: MSCs promote the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues by secreting growth factors such as VEGF and HGF. These factors stimulate the proliferation and migration of keratinocytes, the primary cell type involved in the formation of the epidermis, helping to restore the normal structure and function of the skin.
Potential Benefits of MSC Therapy for Psoriasis
MSC therapy offers several potential advantages over traditional treatments for psoriasis:
- Targeted Immune Modulation: Unlike broad-spectrum immunosuppressants, MSCs specifically target the dysregulated immune pathways involved in psoriasis, potentially reducing the risk of side effects.
- Long-term Remission: Early studies suggest that MSC therapy could offer long-lasting relief from psoriasis symptoms, reducing the need for continuous treatment.
- Minimal Side Effects: MSCs are generally well-tolerated, with a lower risk of adverse effects compared to traditional immunosuppressive therapies.
Conclusion
The use of MSCs, particularly UMSCs, in the treatment of psoriasis represents a promising new frontier in regenerative medicine. By addressing the underlying immune dysregulation that drives psoriasis, MSC therapy could offer a more effective and sustainable treatment option for patients. While further research is needed to refine treatment protocols and fully understand the long-term benefits, the current evidence suggests that MSCs could play a crucial role in the future of psoriasis management.
References:
- Diotallevi, F., et al. (2022). Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Psoriasis: Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci, 23(23), 15080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315080
- Yang, J., et al. (2023). Therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells and their derivatives in common skin inflammatory diseases: Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Front Immunol, 14, 1092668. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1092668